

Method B - US EPA AP-42 industrial wind erosion If the data set has substantial gaps (more than 10% missing), you should contact us to determine the best approach for the site. If the missing data are less than 10% of the total annual data, it is reasonable to either ignore the missing data, or estimate missing daily data by averaging the last measured value immediately prior to the data gap and the first value after the gap. It is possible that some data may be missing from the downloads. You must then input this data into the “Precipitation data input” tab. csv file with the daily meteorological data.
#STOCKPILE AREA CALCULATOR DOWNLOAD#
If using downloaded climate data, you will need to download one annual. You can obtain the daily total precipitation/snow on the ground data for the nearest weather station from the Government of Canada historical climate data site, or from an on-site weather station. Divide the number of months with wind speed more than 19.3 km/h per 12 months and multiply by 100, you obtain the average percentage of time 'I' during the year that wind speed exceeded 19.3 km/h.Find the months with "Wind: Speed (km/h)" more than 19.3 km/h.Scroll down to the “Wind” table, find the “Wind: Speed (km/h)" row and then go across the month columns.Click on the tab labelled “Normals Data”.
 Click on the appropriate station from the list displayed (or the nearest one). Click on the search method that you would like to use (Search by Station Name, Province or Proximity), enter the information requested and click ‘Go’. Go to the Government of Canada’s historical climate data portal. To find the number of days per year with wind speed more than 19.3 km/h: You can then input the information for the wind factor 'I' as a user defined value into the “Input data” tab. If the data set has substantial gaps (more than 10% missing), you can contact ECCC to determine the best approach to use for the site.Īlternatively, if hourly wind data are not available for the site, you can use the 30-year climate normals for the nearest climate station in order to estimate an average wind factor as described in the following steps. If the missing data are less than 10% of the total annual data, it is reasonable to either ignore the missing data, or estimate missing hours by averaging the last measured value immediately prior to the data gap and the first value after the gap. You must then enter this data into the “Hourly wind speed data input” tab. csv files to compile the weather data summary for the reporting year. If you are using downloaded climate data, you will need to individually download 12 monthly. You can obtain the hourly wind speed data for the nearest weather station from the Government of Canada historical climate data site, or from an on-site weather station. Method A requires the determination of a site-specific wind factor (I) and total precipitation/snow on the ground factor (P) for the reporting year. Table 1: Default silt content values used in the calculator for Method A (MDAQMD, 2000) Stockpile material You are also able to enter a site-specific silt content, if you have this information. The Emissions Calculator determines the exposed surface area based on the footprint area and defined active area, where applicable.ĭefault silt content values are included in the calculator, as summarized in Table 1. A = exposed surface area of stockpile (m 2). The total emissions are then calculated by multiplying the EF by the exposed, active surface area.įor conical stockpiles, calculate the exposed area using: I = percentage of time with unobstructed wind speed >19.3 km/h in percent (%).
Click on the appropriate station from the list displayed (or the nearest one). Click on the search method that you would like to use (Search by Station Name, Province or Proximity), enter the information requested and click ‘Go’. Go to the Government of Canada’s historical climate data portal. To find the number of days per year with wind speed more than 19.3 km/h: You can then input the information for the wind factor 'I' as a user defined value into the “Input data” tab. If the data set has substantial gaps (more than 10% missing), you can contact ECCC to determine the best approach to use for the site.Īlternatively, if hourly wind data are not available for the site, you can use the 30-year climate normals for the nearest climate station in order to estimate an average wind factor as described in the following steps. If the missing data are less than 10% of the total annual data, it is reasonable to either ignore the missing data, or estimate missing hours by averaging the last measured value immediately prior to the data gap and the first value after the gap. You must then enter this data into the “Hourly wind speed data input” tab. csv files to compile the weather data summary for the reporting year. If you are using downloaded climate data, you will need to individually download 12 monthly. You can obtain the hourly wind speed data for the nearest weather station from the Government of Canada historical climate data site, or from an on-site weather station. Method A requires the determination of a site-specific wind factor (I) and total precipitation/snow on the ground factor (P) for the reporting year. Table 1: Default silt content values used in the calculator for Method A (MDAQMD, 2000) Stockpile material You are also able to enter a site-specific silt content, if you have this information. The Emissions Calculator determines the exposed surface area based on the footprint area and defined active area, where applicable.ĭefault silt content values are included in the calculator, as summarized in Table 1. A = exposed surface area of stockpile (m 2). The total emissions are then calculated by multiplying the EF by the exposed, active surface area.įor conical stockpiles, calculate the exposed area using: I = percentage of time with unobstructed wind speed >19.3 km/h in percent (%). 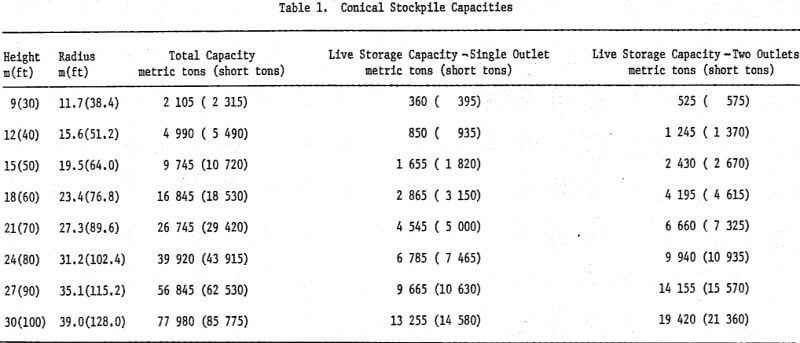
The Calculator avoids double counting when further total precipitation accumulate on days with snow on the ground. P = number of days during the year with at least 0.254 mm of total precipitation (sum of total rainfall and the water equivalent of the total snowfal in mm) and days with snow on the ground.s = average silt loading of storage pile in percent (%).J = particulate aerodynamic factor with the following values:.The Emissions Calculator uses the following equation as the default method to calculate the annual particulate emission factor (EF) for elevated stockpiles and flat stockpiles that are infrequently disturbed:ĮF = 1.12x10 -4 x J x 1.7 x (s/1.5) x 365 x ((365-P)/235) x (I/15) Method A – Annual wind erosion emissions from stockpile surfaces







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
